WiFi networks are everywhere these days. The majority of home users, as well as many businesses, employ a wireless network to provide flexible and convenient Internet access. There are a variety of software and hardware tools available which enable you to gain information about your own and nearby WiFi installations. One of the most useful is a WiFi network scanner.
What is a WiFi Scanner?
A WiFi scanner is a tool that enables the user to discover the details related to nearby WiFi networks. Many WiFi scanners are software applications, but there are also hardware implementations that possess the same functionality. In some cases, a hardware device may be more convenient than a program that requires the use of a computer in order to be useful.
We will be concentrating on the software side of WiFi scanners for the Mac and will point out some specific applications later in this article. We will be using a MacBook Air and the NetSpot WiFi scanning app to illustrate the features and uses of a Mac WiFi scanner. Most quality WiFI scanners will report essentially the same information.
What Information Can be Acquired with a WiFi Scanner?
There is a wealth of knowledge regarding the surrounding WiFi networks that can be obtained through the use of a WiFi scanner app. As its name implies, the tool scans the environment and detects the presence of WiFi networks. When you start up the application it discovers and lists all of the WiFi networks within range of your computer’s wireless antenna.
Using NetSpot’s display for illustrative purposes, we will take a look at the diverse information that the WiFI scanner reports regarding the wireless networks it discovers.
- SSID – The Service Set Identifier (SSID) is the name of the WiFi network. The SSID can be hidden, in which case a client who wants to connect must already know the name of the network. The name can also be sent through the beacons of the access points, enabling anyone who sees the network to attempt to gain access.
- BSSID – The Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID) is the access point’s MAC address.
- Alias – This field will indicate if the network has an alias, and if so, will display it.
- Channel – The channel that the wireless network is currently using for transmission is displayed on the channel field.
- Band – The band field displays the frequency being used by the WiFi network. While 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies have been standard, newer networks may also operate on the 6 GHz band, providing more channels and less interference for Wi-Fi 6E compatible devices.
- Security – This essential field indicates what type of security is protecting a given network. If you are using a WiFi scanner to find networks that are easily accessible, you would like to find an open network. If WEP is the type of security being used, the network can be compromised fairly easily by hackers. WPA2 and WPA3 security provide enhanced protection and are very difficult to crack. You want your network to use this type of security to protect the data and devices which are connected to it.
- Vendor – Here you will find the manufacturer for the WiFi router that is providing the network.
- Mode – This field shows the wireless standard that the router supports , such as 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac, or 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6). Each standard determines which frequency bands are supported; for example, 802.11n can operate on 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, while 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) can operate on 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, or 6 GHz bands.
- Level (SNR) – This field reports the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of the queried network. It compares the level of the WiFi signal to the level of background noise.
- Signal – The strength of the network signal is displayed in this field.
- Signal % – This field shows the percentage of signal strength. The next three fields show the average, maximum, and minimum signal strengths.
- Noise – Here you can see how much noise is impacting a particular network. The next field reports on the noise percentage.
- Last seen – Here you will see how long it has been since your WiFi scanner could see a particular WiFi network.
Why Should I Use a WiFi Scanner?
There are a number of reasons that might cause you to employ a WiFi scanner app. Some of the most common ones include:
Locating available WiFi networks – Using a WiFi scanner, you can find wireless networks within range of your computer or device. If it is an open network, you can use it to gain network access. Scanning from your home or office will also show you wireless signals which are entering your own WiFi coverage area and may impact your network’s performance.
Installing a wireless network – During installation of a WiFi network, a network scanner can help you locate the proper positioning of your router and other network equipment. Scan from various locations in your intended coverage area to determine if the signal will allow the connectivity that you desire. You can conduct a survey that will produce a heat map which indicates the strength of the WiFi signal throughout the surveyed area. Make sure that the scan shows that you have set security and encryption to at least the level of WPA2.
Optimizing a WiFi network – Undertaking a periodic and methodical scan of your WiFi network’s coverage area can be instrumental in maintaining and optimizing its performance. You might discover that areas which previously received strong signals have been impacted by changes in the environment. Scanning will allow you to tune your access points and router location to have your WiFi network performing at the peak of its capabilities. You might find that nearby networks are using the same channel as you and a simple change may make a big difference in network speed.
Identifying rogue access points – Scanning from outside your projected coverage area can alert you to the presence of rogue access points. The wireless signal may exceed the physical boundaries of your home or office. This makes it possible for that van parked outside your building to be attempting to hack into your network. This is another reason that exhibits the need for securing and encrypting your WiFi network.
WiFi Scanners for macOS
Here are some network scanners for the Mac. Similar tools can be found for the operating system of your choice.
NetSpot
NetSpot is a comprehensive WiFi scanner available for macOS that provides a full suite of network scanning and monitoring tools. Whether you’re planning a new wireless network or looking to optimize an existing one, NetSpot can assist you by creating detailed headmaps that clearly show where your signal is the weakest, collecting information about nearby WiFi networks that could be interfering with your own network, and more.
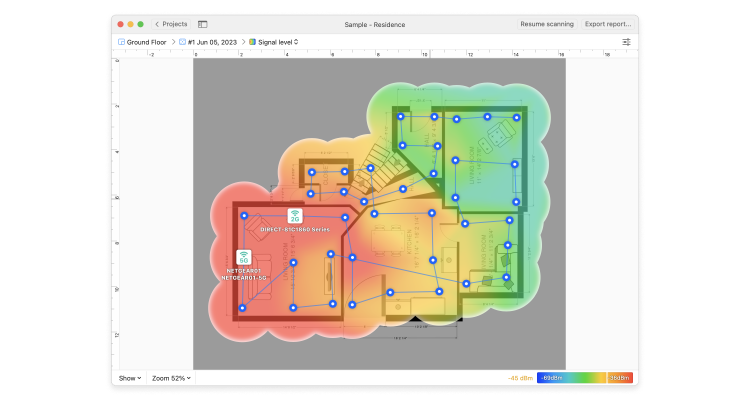
By combining a user-friendly interface with robust wireless network scanning capabilities, NetSpot is an indispensable tool for both casual users and network professionals.To begin enhancing your network today, download NetSpot for free directly from the official website.
KisMac2
KisMac2 is a free WiFi scanner for macOS. It is an open-source, freeware app that is designed to be used by experienced network professionals. It provides details on channel usage, security settings, and signal coverage.
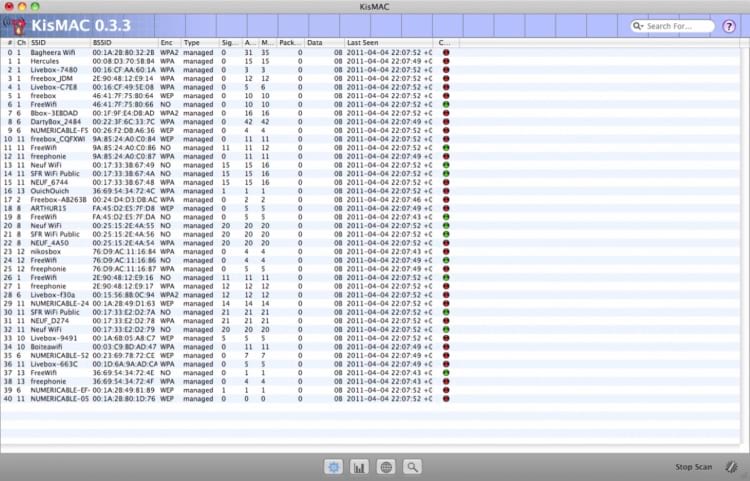
The tool has other uses and can be used to capture packets from an identified network.
iStumbler
Another WiFi network scanner for the macOS is iStumbler. It lists all visible networks and provides their complete details. Double clicking on a network seamlessly opens a connection monitor.
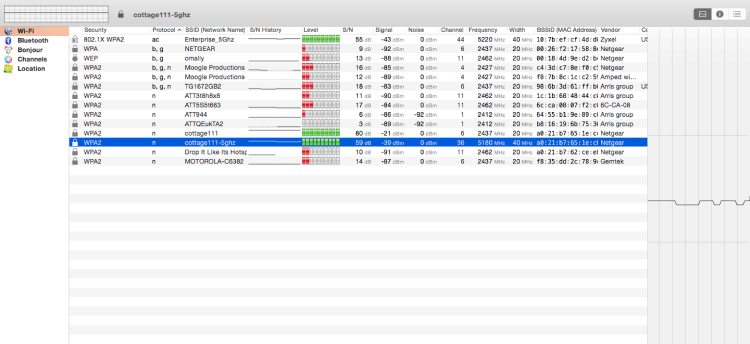
This app features an interactive user interface which uses graphical displays to present network information. It is a paid application but can be downloaded and tested for free.
WiFi Scanner
This is a paid application available through the Apple App Store. It provides all of the WiFi network scanning functionality that you need to discover nearby networks and help tune your own.
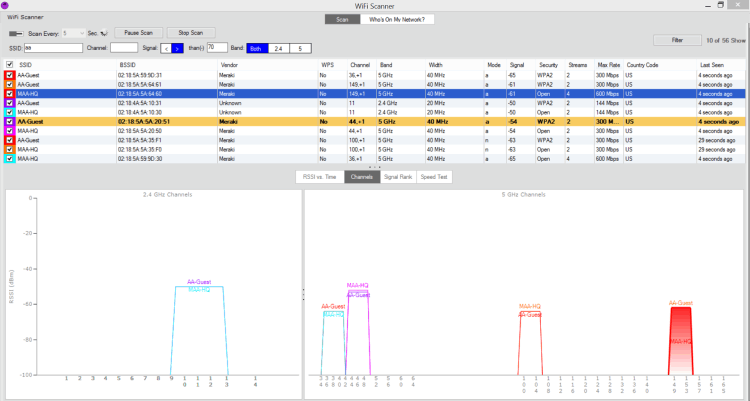
You can also use the app to perform speed testing to verify your Internet connection performance.
***
One of these applications should work for you in your endeavor to scan WiFi networks with your Mac. Whether you are setting up a new network, trying to locate possible access points, or optimizing the performance of your own installation, a WiFi network scanner is an indispensable tool.