In this article, we are going to talk about the practice of wardriving, which needs to be done with the proper software. We will illustrate how to use KisMAC for this purpose. The information we provide is meant for educational purposes only. We do not condone accessing wireless networks without authorization, and wardriving can be used to accomplish this feat.
What is Wardriving?
Wardriving, or war driving, involves physically searching for open or unsecured wireless networks that can be easily accessed. The term originates from the movie “WarGames” where the practice was called wardialing. Though wardriving implies that a motor vehicle is used to search for the networks, it can be done while walking or riding a bike. Wardriving may also be known as access point mapping. This is because the wardriver is identifying potential access points that can be used to connect to a wireless network.
Simply surveying a locality with the intention of collecting data on available wireless networks is not illegal in the U.S. Accessing networks that are discovered and are not meant for public use can be considered a crime in many different countries. The seriousness of the transgression may take into account the purposes for which the wardriver used the compromised network.
A successful wardriver who has gained access to your network may have done so for malicious reasons. Their intention may be to attempt to steal sensitive data such as banking information. They may want to install malware that allows them to exert control over your machine and use it however they wish. If you want to make your network less appealing to a potential wardriver, ensure that you are using the highest level of security that you can. Your network should be protected by either WPA2 or WPA3 encryption.
Tools for Wardriving
In order to perform wardriving you need some hardware and software tools. There are several pieces of equipment that you need. They are:
- A mobile computing platform – You cannot pursue wardriving from a stationary location. For this reason, you need to use a mobile device or laptop on which the software to scan for networks will be installed. Some appropriate applications can run on smartphones or tablets. This platform manages the wardriving enterprise and is used to defeat network encryption.
- Wireless network card and antenna – This component is used to remotely monitor and search for wireless networks. The mobile device may provide these items, but in some cases, additional hardware is used to increase the wardriver’s scanning power.
- GPS system – A GPS is required to pinpoint the exact location of the discovered WiFi routers. Once again, the mobile device may contain this component, negating the need for additional equipment.
In addition to the hardware requirements, you need software that is capable of cracking the passwords on WEP and WPA encrypted networks. There are many different software tools which can be used for this purpose. For this article, we will be concentrating on using KisMAC as the software component used for wardriving efforts. Using KisMAC necessitates the use of a laptop running macOS, as the software only supports this platform.
Configuring KisMAC for Wardriving
First, you need to download KisMAC and install it on your laptop. Once this is accomplished you need to configure the tool so it can be used for wardriving. KisMAC’s interface is relatively easy to navigate, and the interface displays information regarding wireless networks within range of your system. You can sort this information in various ways such as to determine which available networks have the weakest encryption implemented. The number of packets transmitted as well as their size can also be obtained from the KisMAC display.
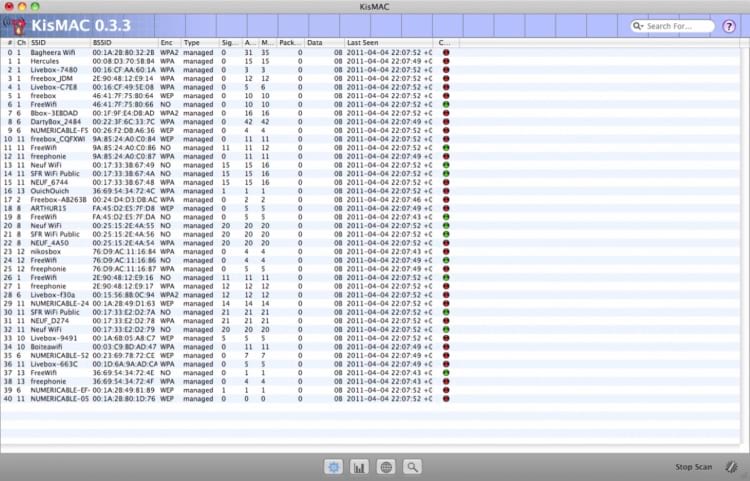
There are certain preferences that should be set if you intend to use the tool for wardriving. They include:
- Scanning options – The scanning options control the way KisMAC behaves when you close the application. If you want to ensure that you do not accidentally lose data, it is recommended that you leave the “do not ask to save data on exit” box unchecked. This way you will be prompted to save your work when closing the app.
- Filter – The filter option allows you to enter a wireless network’s MAC address to exclude them from your results. This can be helpful for removing uninteresting networks from your scanning procedure.
- Driver – Here you select whether you want your system to scan in active or passive mode. Depending on your intentions at the time, either mode may be appropriate. Passive attacks are more difficult for the target to detect. This option also lets you select the network card to be used by KisMAC.
- Traffic – Use this option to determine how the average signal strength will be calculated for the networks under consideration. You can set a time value from 1 to 300 seconds. A larger number will supply more accurate details about the network.
Mapping Wardrives Using KisMAC
Once you have configured KisMAC, you are ready to use the tool for mapping wardrives. Some other tools create a map from your wardriving efforts. KisMAC requires that a map be imported prior to starting a wardriving session.
Before importing a map, you need to tell KisMAC the latitude and longitude of the center of your wardriving area. While this data can be entered manually, using a GPS is the preferred method. To connect a GPS to KisMAC, follow these steps:
- Connect the GPS to your laptop. You may need to use a serial to USB converter cable for this purpose.
- Select use CoreLocation to get coordinates in the KisMAC GPS preferences.
- Choose use GPS coordinates in the GPS preferences.
- Select your tracing options.
Once the GPS is connected and configured, you are ready to import a map. Follow this procedure:
- Select File from the main KisMAC menu.
- Choose Import and then Map from Server.
- In the Download Map dialog box which will open, you can select the server and the type of map you wish to import. Your GPS coordinates are automatically imported into this dialog box.
- Select File and Save Map to protect yourself if the application crashes by saving your map.
- Waypoint 1 is set to your current location but you need to set a second waypoint before starting the wardrive. Select Map from the menu and then Set Waypoint 2. This can be your final destination or any other point on your map.
You are now ready to commence your wardriving activities. Here is what you need to do to get going.
- Click on the Start Scan button. This will start the process of locating potential access points.
- Once you have discovered networks you can use the options available in KisMAC to view more detailed information concerning a specific network.
- The Graph option allows you to track the data transferred over the network by bytes, packets or signal.
- The Map option lets you see a live map of your current wardrive.
The information obtained during a wardrive enables the driver to identify prospective networks that may be susceptible to attack. Unlike some wireless scanning tools, KisMAC also has the capability to perform attacks against encrypted networks using reinjection, brute-force, or wordlist techniques. At this point, you may be crossing the line between harmless information gathering and using that data for malicious intent.
As you can see, KisMAC is a versatile tool that can be used for wardriving on a MacBook. It also has other, more traditional uses, such as performing penetration testing and analyzing your network. We hope you have found this information useful.